|
WHAT IS RADIATION ?
Uzm.Dr.Kamuran Kuş
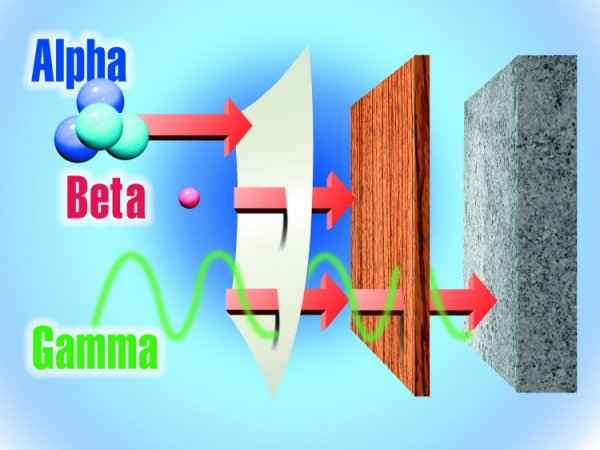
Radiation is the
emission or transfer of energy in the form of electromagnetic
waves or particles. As it is known, the main structure of matter
is made up of atoms. On the other hand, atom consists of a
nucleus comprised of protons and neutrons, and electrons moving
around it. If the number of neutrons in the atom nucleus of a
substance is more than the protons, these substances show unsteady
structure and the neutrons change in protons by emitting β- rays
(negatrons). If the protons are more than neutrons a proton
changes into a neutron emitting β+ rays (positrons). Neutrons
and protons in the exited states of the nucleus deexcite to the
ground state by emitting γ- rays. Heavy Nucleic may emitt α-
rays (Helium nuclei) or may undergo fission reaction. The
substances which undergoes these changes spontaneously are
called radioactive substances , and the rays emitted to the
environment such as alpha, beta and gamma are called radiation.

DAMAGES OF RADIATION
X rays, ultraviolet
rays, visible rays, infra-red rays, micro waves, radio waves and
γ-rays are the different regions of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The regions of the spectrum are defined with their frequencies
and wave lengths. Since x rays and γ- rays and have very high
frequencies, such radiation have the energy to break the
chemical bonds or ionize subtances. Such radiation is called
ionizing radiation.
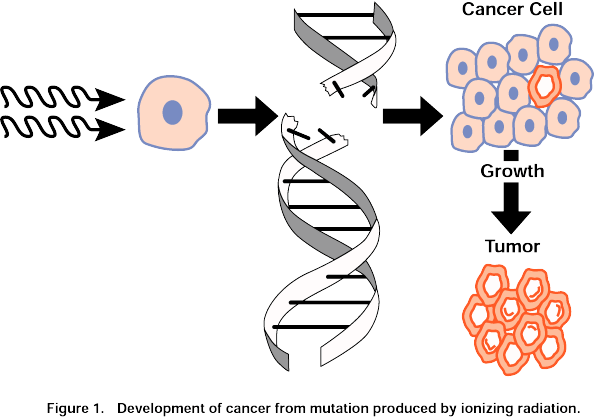
Ionizing is capable of
fragmenting the DNA, the genetic material of cell. Damaging of
DNA kills the cells. As a result, the tissue is damaged. A
little damage in the DNA gives rise to permanent changes which
may cause cancer.
Radioactive
contaminants negatively effect the life of human beings, animals
and plants and disrupt the environment and ecological balance.
In addition, radiation caused genetic changes in lively beings.
The effect of radiation varies depending on the type of
radiation, age and organ. Eyes are most affacted by type of
radiation causing sight weakness, cataract and slowing of eye
concord. On the other hand, skin is more resistant against
radiation. The damages of radiation become noticable generally
late, and the effect only becomes observable with deaths caused
by atom bombs and burns in high radiation exposure dramatically.
X rays are high energy
radiation which causes the materials they contact to lose
electrons, in other words to become ionized. These rays are used
for taking x rays used for diagnosis purposes. The cells which
are most sensitive to the ionized radiation including x-rays are
the fast divided cells and therefore developing fetus and the
tissues of it are the structures expected to receive the most
damage from these rays. The important point here is that only
the tissue contacting with the ray is affected and these rays
can travel through the body. For instance, the rays received
from a hand x ray taken can not progress within the body and
reach the uterine.
IS X RAY HARMFUL DURING PREGNANCY?

As in all diagnosis
and treatment methods, there are potential benefits and damages
in x rays. This is valid for both pregnant and non-pregnant
women.
Since ionized
radiation have more destructive effect in fast diving and
reproducing cells, the developing fetus may be negatively
affected. Nevertheless, it should be noted that these effect
depent on the dose and duration.
The effects according to the pregnancy week during which a
person is subjected to radiation are as follows:
-
Malformation and prenatal death: The most sensitive period is 8 days
after the impregnation. The radiation received in this
period causes miscarriage in 50-75% of the pregnancies,
while most these miscarriages are not noticed generally,
since they precede the expected menstrual bleeding. On the
other hand, the rate of miscarriages in clinically noticed
pregnancies is about 15-20%.
-
Developmental lag:
Another most sensitive period is the 8th-56th
days after the impregnation. In researches made over the
people who survived the atom bomb in Japan, it has been
detected that the women who were exposed to about 25
radiation in their pregnancies during this period, gave
birth to shorter, lighter babies with smaller head radius.
-
Neurologic effects: the most sensitive period is 2nd-15th
weeks after the impregnation. Again, according to the
observations made over those who survived the atom bomb, it
has been detected that the mostly encountered abnormally was
the small head which is called microsephaly. Microsephaly
generally accompanies mental retardation, but mental
retardation was found only 25 % of the phenomena of
microsephaly emerging due to radiatin.
-
Severe mental retardation: Another
most sensitive period is the 8th 15th
weeks. It has been detected that severe mental
retardation of 0.4% as per each radiation exposed occurred
in babies delivered by women who were exposed to radiation
in the 8th, 15 th weeks of pregnancy. A decrease of 25 ponts
in IQ level is observed as a per each 100 radiation in
babies who were exposed to radiation during 8th
25th weeks of pregnancy. In these babies, also
epilepsy disease is more frequently seen in later periods of
their life.
-
Cancer:
The most feared effect of radiation is cancers which emerge
in the long term.

Source:
Exposure of the Pragnant Patient to Diagnostic Radiation A Guide
to Medical Management 2nd edit. by Louis K Wagner, Richard G.
Lester and Luis R. Saldana, 1997, Medical Physics Publishing,
Madison, Wisconsin.
EARTQUAKE IN JAPAN

The concerns over the nuclear plants in Japan damaged after the
earthquake are growing. The radiation arising from the nuclear
plants poses hazard to the human health in the short or long
term.
The effect of radiation on human health are birefly as follows:
It has been reported that the level of radiation around Tokyo is
less than 1000 milisievert. That this rate is 10.000 times
bigger than normal radiation fund.
A person is exposed to micro 10 milisievert radiation during a
dental x-ray taking.
People may receive radiation from the environment. Flights,
routine chin and dental x-rays, MR and tomography are also ways
of receiving radiation.
A flight over 40 thousand feet causes 3 to 9 milisievert
radiation in one hour depending on the course of flight.
Generally, a human receives annually 1 to 10 milisievert from
the air and land.
During computer aided tomography of the whole body one receives
a dose of 20-30 milisievert radiation, and tomography of a
single organ the dose received is 10 milisievert. The sievert
unit is used for measuring radiation and it indicates the amount
absorbed by human tissues. One sievert equals to one thousand
milisievert.
According to U.S.A. Environment Protection Agency, the different
radiation levels by milisievert unit and the effects of this
over the human health are as follows:
The chemistry of blood changes in those exposed to 50-100
milisievert radiation.
500 milisievert causes nausea in hours.
700 milisievert: vomiting
750 milisievert: Hair loss for 2-3 weeks.
900 milisievert: Diarrhea
1 000 milisievert: bleeding
4 000 milisievert: Possible death within 2 months if no
treatment is made
10 000 milisievert: destruction in intestines, internal bleeding,
death within 1-2 weeks.
20 000 milisievert: destruction in central nerve system and loss
of consciousness within hours or days
Source:
Taiwan Atom Energy Agency; World Nuclear Union; US.A.
Environment Protection Agency.
5.
Web sayfasının dizaynı Aytuna Devrim Canbul tarafından
yapılmıştır.
Menu |
E-Posta
| Bilkent
Üniversitesi Ana Sayfası
|
|



